11 Home Remedies For Fungal Skin Infections & Prevention Tips
Put an end to this skin ailment with ingredients already in your kitchen.

It is important to try various medicinal techniques, both internal and external, to get rid of fungal skin infections. Research states that over a billion people usually suffer from hair, skin, or even nail infections caused by fungus or other bacteria. In addition, over 1.5 million people worldwide encounter a serious fungal issue accelerated by diseases like aids, tuberculosis, or any form of cancer (1).
Many make the mistake of ignoring the initial signs of white marks on their body as it causes no itch or pain in the beginning. Unfortunately, it only increases and flares after a while and causes extremely painful encounters in the long run. Consult your doctor for anti-fungal creams or oral medication, depending on the severity of the situation. In case of a mild infection, you can resort to some natural and organic ingredients to help cure them. Keep scrolling to more about these remedies!
In This Article
What Is A Fungal Infection?
A fungal infection is a common infection of the skin that is a result of a fungus invading an area of your body. Your immune system will try to ward off this infection initially, but when it becomes too much for the immune system to handle, it results in a fungal infection.
Fungi can survive anywhere – be it the air, soil, or water. Certain fungi also survive naturally in the human body. Like many microbes living in your body, there are both good and bad fungi living in there. While some of them may be beneficial, others can turn out to be harmful.
There are different types of fungal infections, and the symptoms of each type may vary.
Types And Symptoms Of Fungal Infections
The common types of fungal infections are as follows:
- Athlete’s Foot: It is also commonly referred to as tinea pedis, and it often affects the foot. Such fungal infections are quite common in athletes as the fungi can thrive perfectly in warm and moist environments like the socks and shoes worn by them. The symptoms of athlete’s foot include:
- Blistering
- Redness
- Softened skin
- Peeling of skin layers
- Scaly skin
- Itching, stinging, or a burning sensation
- Yeast Infection: Vaginal yeast infection is another common type of fungal infection. It is triggered by a type of fungus called Candida albicans. A Candida overgrowth often disrupts the balance of the vaginal flora. It is also capable of causing toenail infections and diaper rashes. The symptoms associated with a yeast infection include:
- Swelling and/or itching around the vagina
- A burning sensation or pain while urinating or during intercourse
- Redness/soreness around the vagina
- An unusual vaginal discharge
- Jock Itch: This condition is medically known as tinea cruris. Since fungi love moist and warm areas, they can easily affect certain areas of your body like the groin, buttocks, and inner thighs. This type of infection is more common in summer and warm/humid parts of the world. Its symptoms include:
- Redness
- An itching or burning sensation
- Chafing of the skin in the affected area
- A red rash with raised edges
- Peeling or cracking of the skin
- Ringworm: It is also referred to as tinea corporis. This type of fungal infection is triggered by fungi that thrive on dead tissues like nails, hair, and dead skin. These fungi are also known to cause jock itch and athlete’s foot. However, if the infection occurs anywhere else on your body, it is referred to as a ringworm. The symptoms associated with it are:
- A red, scaly, and ring-shaped patch with raised edges
- Fissures
- Skin darkening
- Blistering
Let us now look into the causes of a fungal infection.
Causes And Risk Factors For A Fungal Infection
As we have already mentioned, fungal infections are caused by yeasts (such as Candida or Malassezia furfur) or by dermatophytes like Epidermophyton, Microsporum, and Trichophyton. An infection begins when the fungal spores touch certain areas of your skin or if the fungus is inhaled.
Some factors can also put you at an increased risk of developing a fungal infection. They are as follows:
- A weakened immune system
- A genetic predisposition to fungal infections
- Being in a profession that causes you to sweat a lot (e.g., an athlete)
- Close contact with an affected individual
- Obesity – Obese people tend to have more skin folds, which are perfect spots for a fungal infection.
As you can see, many factors could contribute to the onset of a fungal infection in an individual. Antifungal topical formulations are one of the most sought-after ways to combat such an infection. There are also a number of home remedies that may help in the treatment of mild to moderate cases of fungal infection. They are as follows.
Home Remedies To Treat A Fungal Infection
1. Coconut Oil
You Will Need
1-2 teaspoons of organic coconut oil
What You Have To Do
- Apply coconut oil to the affected area. Leave it on for 30-40 minutes
- Rinse it off.
- You may also leave it on and allow it to dry on its own.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this 1-2 times daily.
Why This Works
Coconut oil is antifungal and can help treat fungal infections, especially the ones caused by Candida (2).
2. Garlic
You Will Need
- 2-3 garlic cloves
- 2-3 teaspoons of organic coconut oil
What You Have To Do
- Mince two to three garlic cloves.
- Add the minced garlic to a few teaspoons of organic coconut oil.
- Heat the mixture over low flame for 4-5 minutes.
- Allow the mixture to cool and strain the oil.
- Apply the oil to the affected area.
- Leave it on for at least 30-40 minutes before rinsing it off.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this once daily.
Why This Works
Garlic contains ajoene, an organosulfur compound that exhibits antifungal properties (3).
3. Apple Cider Vinegar
You Will Need
- 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar
- ½ cup of water
- Cotton balls
What You Have To Do
- Add a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar to half a cup of water.
- Mix well and dip a cotton ball into the mixture.
- Apply the soaked cotton ball to the affected area.
- Leave it on for 20-30 minutes before rinsing it off with plain water.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this 1-2 times daily.
Why This Works
Apple cider vinegar is effective in eliminating a wide range of microbes, including fungi, due to its antifungal nature. A study published in the Journal of Prosthodontics found ACV to be effective against Candida (4).
4. Cranberry Juice
You Will Need
500 mL of cranberry juice
What You Have To Do
Consume 500 mL of cranberry juice daily until the symptoms clear away.
How Often You Should Do This
You may drink this juice once daily.
Why This Works
Cranberry juice is fungistatic. According to a study published in the journal Applied Microbiology, cranberry juice is effective against eight species of dermatophytes (5).
5. Aloe Vera
You Will Need
Freshly extracted aloe gel
What You Have To Do
- Take some freshly extracted aloe gel and apply it to the affected area.
- Leave it on for 20-30 minutes and rinse it off.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this once daily.
Why This Works
The fresh leaves extract of aloe vera possesses antifungal properties. A study published in Mycoses journal shows that aloe vera reduces the growth of Candida, a common fungal species (6).
6. Baking Soda
You Will Need
- ½ cup of baking soda (sodium bicarbonate)
- Water
What You Have To Do
- Add half a cup of baking soda to a basin or bucket filled with water.
- Allow the baking soda to dissolve completely.
- Soak your feet in the solution for 15-20 minutes.
- Alternatively, you can also soak a clean washcloth in the solution and apply it to any of the affected areas.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this 1-2 times daily.
Why This Works
While the mechanism of its action is yet to be explored, a study published in the journal Mycopathologia found that baking soda exhibited antifungal properties (7).
7. Epsom Salt Bath
You Will Need
- 1 cup of Epsom salt
- Water
What You Have To Do
- Add a cup of Epsom salt to a tub filled with water.
- Allow it to dissolve completely and soak in the bath for 15-20 minutes.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this once every alternate day until you notice an improvement in your symptoms.
Why This Works
Epsom salt contains magnesium. Magnesium helps reduce inflammation due to its anti-inflammatory properties and is thus a great remedy to alleviate the inflammatory symptoms of a fungal infection (8).
8. Guava Leaves
You Will Need
- A handful of guava leaves
- Water
What You Have To Do
- Take a handful of guava leaves and place them in a saucepan filled with water.
- Allow it to boil for 15-20 minutes.
- Let the mixture cool. Strain it.
- Use this solution as a soak, bath rinse, or wash for the affected areas.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this once daily.
Why This Works
Guava leaves help inhibit fungal growth and may improve the functions of other antifungal formulations (9).
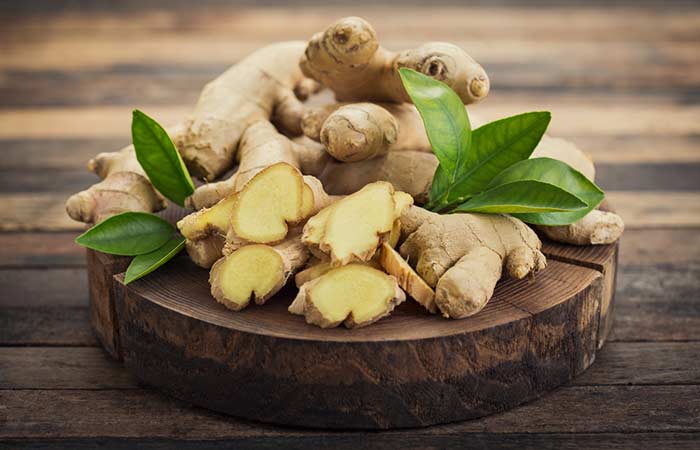
9. Ginger
You Will Need
- 1-2 inches of sliced ginger
- A cup of water
- Cotton balls
What You Have To Do
- Add the sliced ginger to a cup of water. Bring the mixture to a boil in a saucepan.
- Simmer for 5 minutes and strain.
- Allow the mixture to cool.
- Dip a cotton ball in the solution and apply it to the affected areas.
- You can also drink ginger tea for additional benefits.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this 1-2 times daily.
Why This Works
Ginger possesses antifungal and fungistatic properties that may help in preventing the formation of fungi biofilm (10). These properties may also help in getting rid of fungal skin infections.
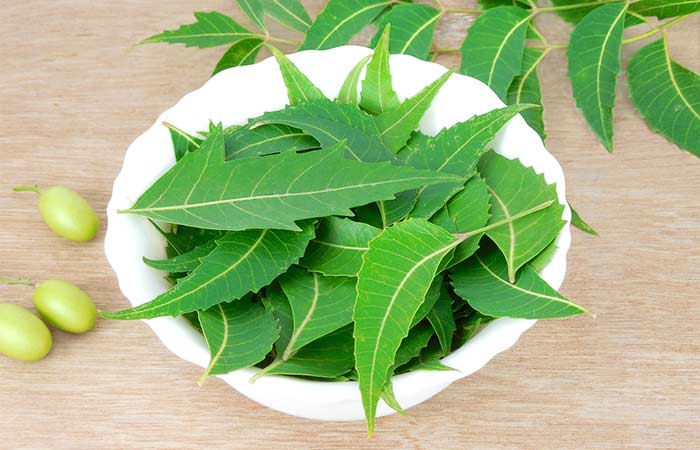
10. Neem Leaves
You Will Need
- A handful of neem leaves
- Water
What You Have To Do
- Take a handful of neem leaves and put them in a saucepan filled with water.
- Bring the leaves to a boil and simmer for 10-15 minutes.
- Allow the mixture to cool and strain.
- Soak a cotton ball in the solution and apply it to the affected areas.
- Leave it on for 20-30 minutes and rinse it off.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this 1-2 times daily.
Why This Works
Neem leaves are rich in polyphenolic flavonoids that exhibit antifungal properties (11). Hence, they may help get rid of fungal infections.
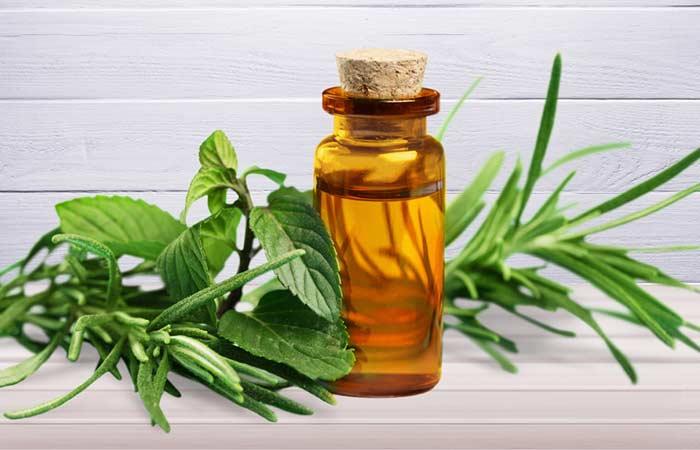
11. Tea Tree Oil
You Will Need
- 2-3 drops of tea tree essential oil
- 1 tablespoon of coconut oil
What You Have To Do
- Add two to three drops of tea tree oil to a tablespoon of coconut oil.
- Mix well and apply it to the affected area.
- Leave it on for 20-30 minutes and rinse it off with water.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this once daily.
Why This Works
Tea tree oil exerts antifungal action (12). This may help you deal with fungal infections.
Once you get a fungal skin infection, it can become a recurring event if proper care and caution are not taken. Listed below are some helpful tips to prevent fungal infections from recurring time and again.
How To Prevent A Fungal Skin Infection
- Wear breathable cotton underwear.
- Follow a good personal hygiene regimen.
- Avoid wearing tight-fitting clothing.
- Keep the folds and corners of your skin clean and dry.
- Avoid vaginal douching.
- Avoid using perfumed soap and scented tampons.
- Manage your stress levels.
In some cases, a fungal infection may be mistaken for psoriasis or bacterial infection. To be able to differentiate a fungal infection from them, you should be aware of the major differences between the three conditions.
Fungal Infection Vs. Psoriasis Vs. Bacterial Infection
The main differences between a fungal infection, psoriasis, and bacterial infection are as follows.
Fungal Infection
• It is caused by fungal spores like Candida.
• It may cause symptoms of itching, redness, peeling, and scaling.
• It is categorized into different types depending on the body part it affects.
Psoriasis
- It is a chronic condition that is triggered by an overactive immune system.
- It causes cells to build up on your skin’s surface, thereby resulting in symptoms like red patches, scales, itching, burning, and swelling of your skin.
- It can be categorized into different types.
Bacterial Infection
- It is triggered by different bacterial species.
- It can cause varying symptoms like cough, fever, nausea, sneezing, cold, and so on.
- Bacterial skin infections cause symptoms like rashes, blistering, redness, pain, tenderness, and itchiness.
- It is classified into different types, depending on the symptoms exhibited and the type of bacteria triggering it.
If you are unsure, it is best to consult a doctor.
Fungal skin infection develops due to a weakened immune system or contact with an infected individual. When yeasts such as Candida or Malassezia furfur get across your skin barrier, it can result in fungal infections such as athlete’s foot, ringworm, or yeast infection. You can use coconut oil, aloe vera, or apple cider vinegar to treat mild infections. To avoid fungal infections from recurring, you must follow a proper hygiene routine and avoid wearing extremely tight clothes. While fungal, bacterial infections, and psoriasis cause red, burning, and peeling skin, they are all caused by different factors. If you see no improvement in your symptoms and you are not sure, consult a doctor.
Hope you found this article informative. Don’t forget to leave your feedback in the comments box below.
Frequently Asked Questions
What kills fungus on the skin?
Any of the remedies discussed above can help in getting rid of fungus on the skin. Antifungal ointments are also effective in treating fungal skin infections.
How long does it take for a fungal skin infection to clear up?
While a superficial fungal infection may heal in a few days or months, a deep tissue infection may take up to two years.
What should you not eat with a fungal infection?
If you have a fungal infection, avoid sugar, white flour, glutenous foods, fermented drinks like alcohol, and certain dairy products like whole milk as they may aggravate the condition. Instead, you can start consuming more of antifungal foods like herbal teas and probiotics like yogurt.
What is the strongest over-the-counter antifungal medication?
Some of the most popular over-the-counter antifungal medications include butenafine hydrochloride, clotrimazole, miconazole nitrate, terbinafine hydrochloride, and tolnaftate.
How to test for a fungal sinus infection?
The common diagnostic tests for fungal sinusitis include total immunoglobulin E test, immunologic testing for allergens, and non-specific allergy testing.
Can I get a fungal infection from not washing my bath?
Bathrooms are the ideal place for fungi to grow as they are both warm and moist. Those susceptible to diseases are thus quite likely to catch a fungal infection from a dirty bath.
When to see a doctor for a fungal infection?
While most fungal infections can be treated with the above remedies and any of the over-the-counter medications, some symptoms may be quite severe and may not show any improvement despite treatment. In such instances, it is best to avail medical treatment immediately.
References
- “Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases—Estimate Precision” Journal of Fungi, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “In vitro antimicrobial properties of coconut oil on Candida species in Ibadan, Nigeria.” Journal of Medicinal Food, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Antifungal activity of ajoene derived from garlic.” Applied And Environmental Microbiology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Antifungal Activity of Apple Cider Vinegar on Candida Species Involved in Denture Stomatitis.” Journal of Prosthodontics, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Antifungal Properties of Cranberry Juice” Applied Microbiology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Aloe vera extract reduces both growth and germ tube formation by Candida albicans.” Mycoses, this US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Antifungal activity of sodium bicarbonate against fungal agents causing superficial infections.” You must Mycopathologia, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Magnesium Decreases Inflammatory Cytokine Production: A Novel Innate Immunomodulatory Mechanism” Journal Of Immunology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Analysis by UPLC-MS-QTOF and antifungal activity of guava (Psidium guajava L.)” Food and Chemical Toxicology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Survey of the Antibiofilm and Antimicrobial Effects of Zingiber officinale (in Vitro Study).” Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Antifungal activity of different neem leaf extracts and the nimonol against some important human pathogens” Brazilian Journal Of Microbiology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Antifungal effects of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil and its components on Candida albicans, Candida glabrata and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.” Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, US National Library Of Medicine.